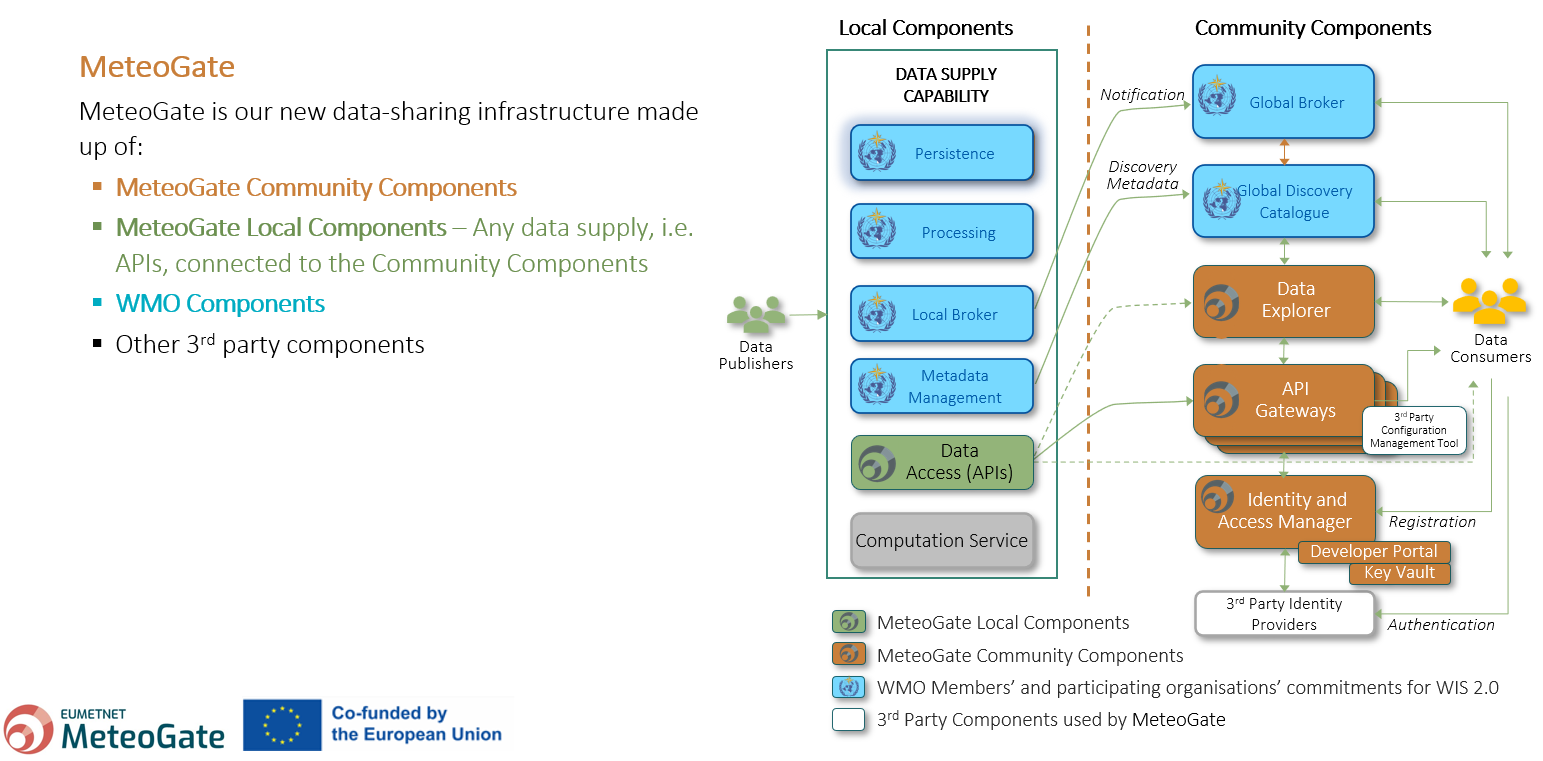
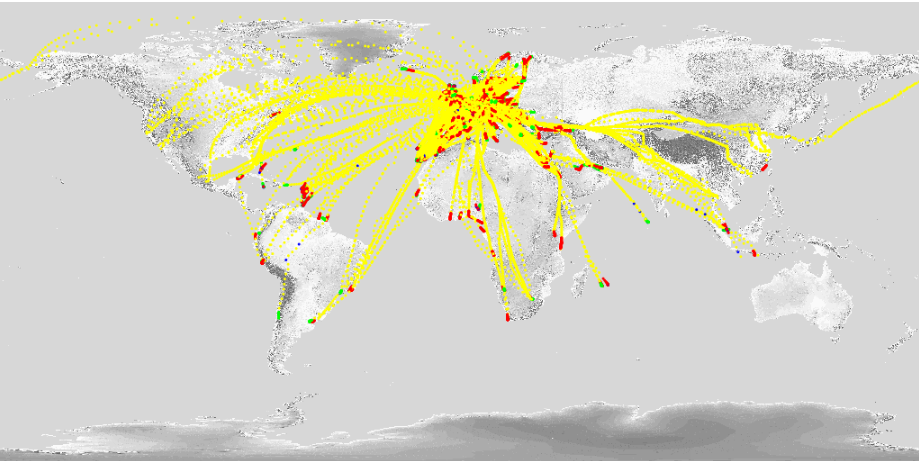
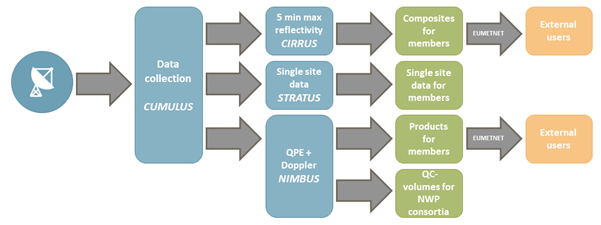
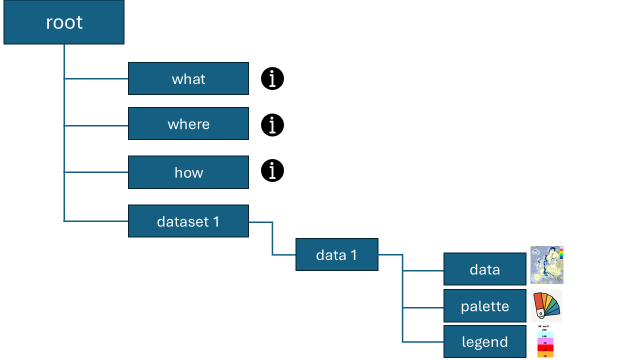
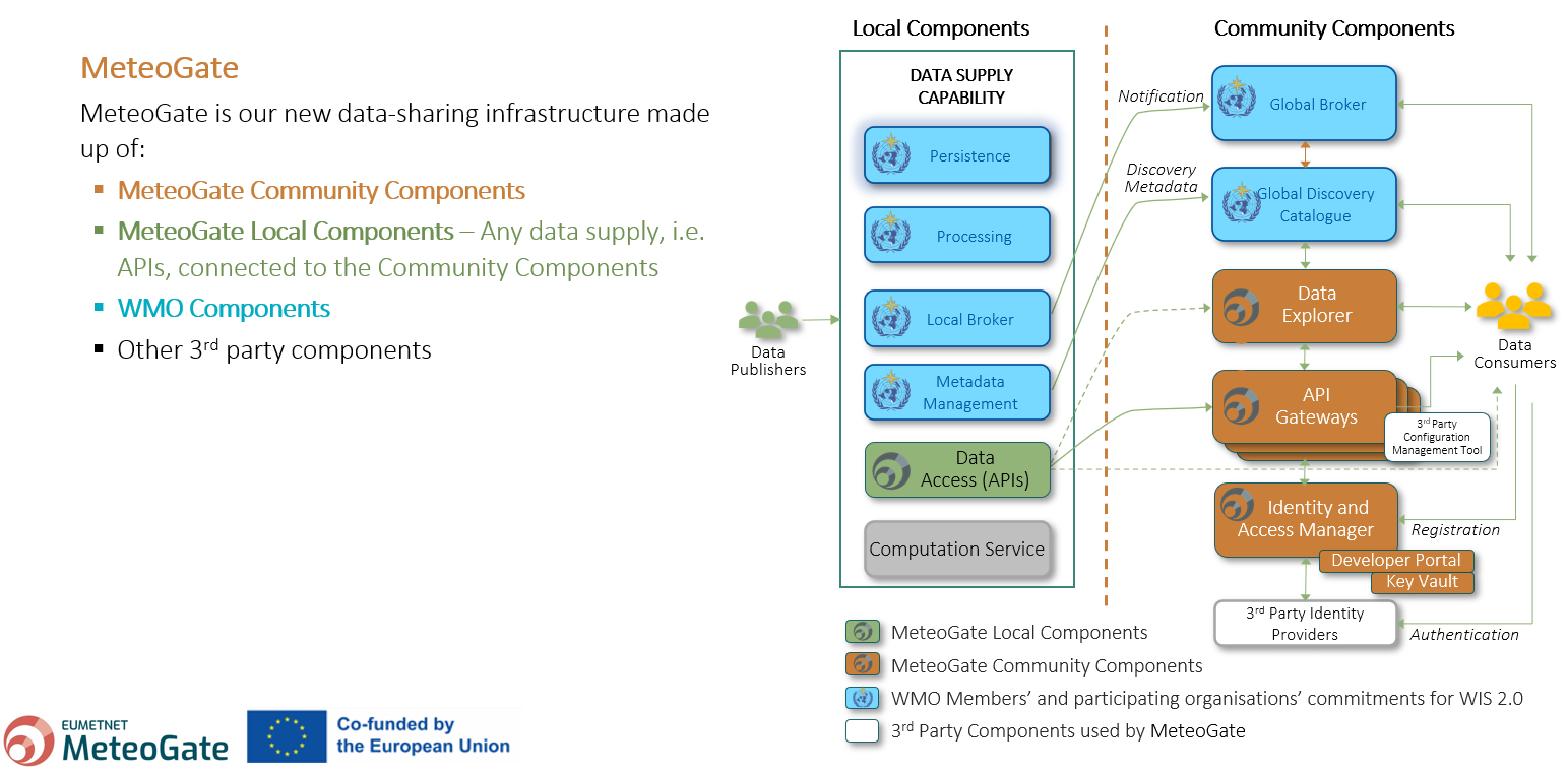
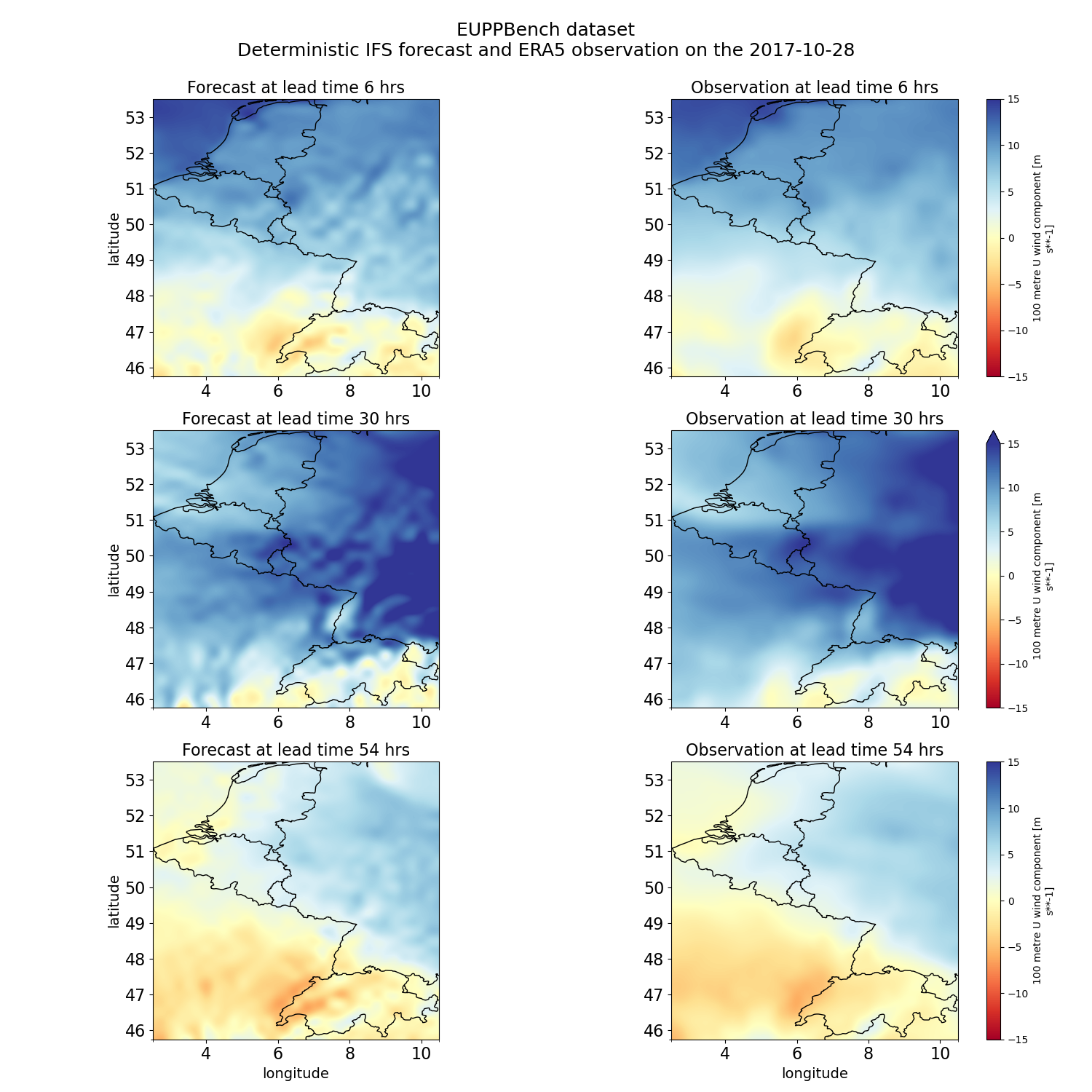
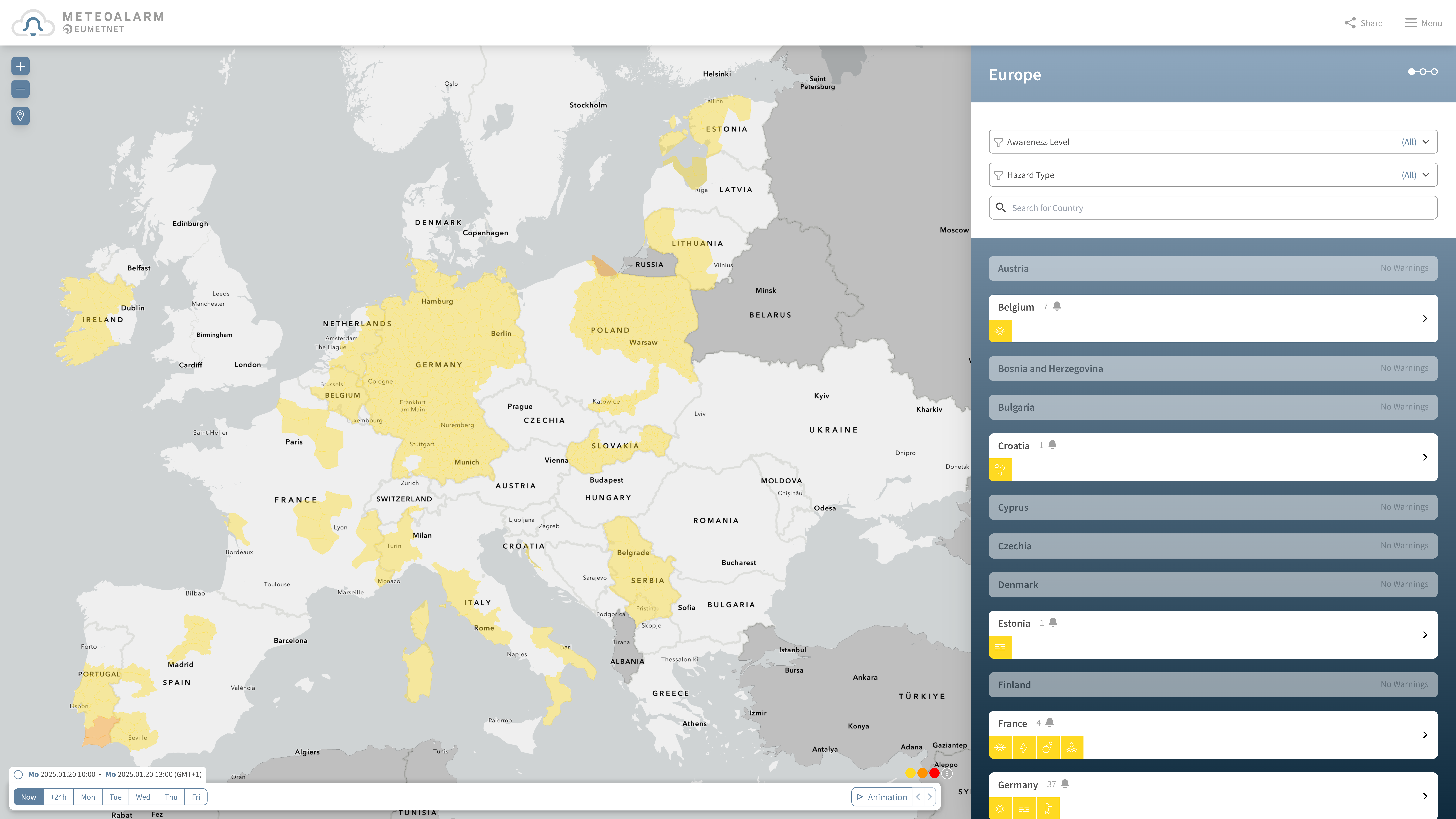
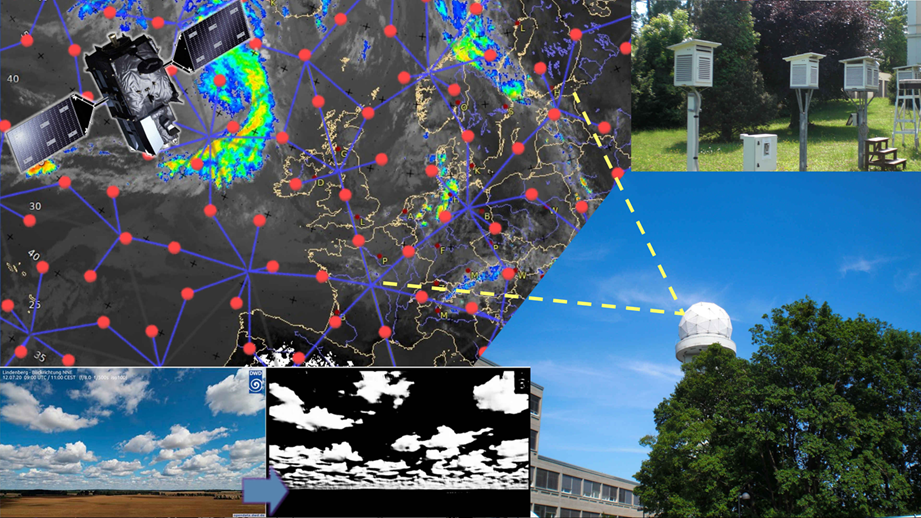
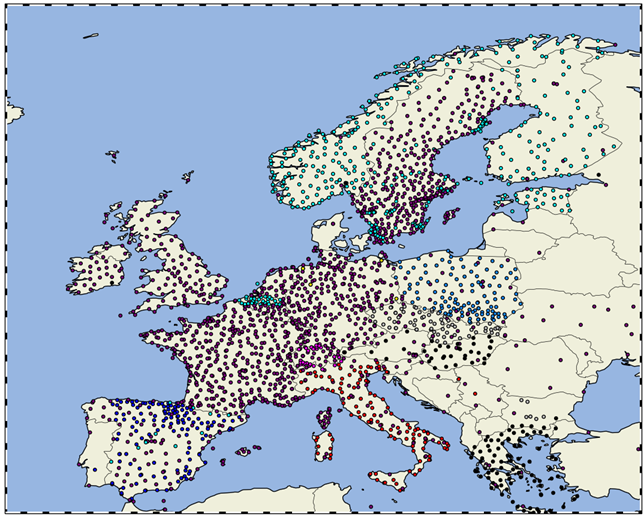
The European Meteorological Society has selected the European Meteorological Aircraft Derived Data Centre (EMADDC) as the recipient of the EMS Technology Achievement Award 2024.
For further information, see the link below:
EMS Technology Achievement Award 2024 for EMADDC : European Meteorological Society (emetsoc.org)