
OBSERVATIONS – E-ABO
Aim
The main aim of the EUMETNET-ABO (Aircraft Based Observations) Operational Service is to fulfil the requirements of the EUCOS Operational Programme for measurements of high quality upper air meteorological variables from aircraft.
Objectives
The continued, sustainable access to high quality upper air observations of temperature, wind speed and direction (and humidity where possible) from commercial aircraft.
Improved uniformity of coverage of airports providing 3-hourly profile observations across the EUCOS domain.
Ensuring the monitoring and reporting of individual network performance to enable the effective combination of the different data sources into one, efficient observing network.
Implementing new capabilities to enable more aircraft based observations to be produced within a reduced data budget.
Continuously seeking to introduce efficiencies via targeted use of cost-effective data sources or transmission methods.
Deliver quality-controlled aircraft-derived data from Mode-S EHS/ADS-B via the EMADDC operated as a service to the EUMETNET community by KNMI.
Flexibility to facilitate the provision of additional data required by individual NMHSs.
Organisation
The current 5-year phase of the E-ABO programme began on 1st January 2024 with the Met Office as the Coordinating Member, working in partnership with KNMI and DWD. KNMI operate the EMADDC for the provision of aircraft derived data from ADS-B/MODE-S EHS data and DWD manage the AMDAR data optimisation and humidity contracts.
Programme Manager: Martyn Sunter, Met Office
Technical Coordinator: David Snook, Met Office
More information
AMDAR
E-AMDAR is EUMETNETs contribution to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Aircraft Meteorological Data Relay (AMDAR) observing system. E-AMDAR facilitates the fully automated collection and transmission of weather observations from commercial aircraft. The E-AMDAR programme is an integrated component of the WMO Global Observing System (GOS) of the World Weather Watch (WWW) Programme . The system is operated by EUMETNET Member NMHS in collaboration and cooperation with partner airlines. Onboard sensors, computers and communications systems collect, process, format and transmit the weather data to ground stations via satellite and VHF radio links. The transmission of this data is most often performed by the aircraft’s ACARS (Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System) system. Once on the ground, the data is then relayed to the global network of national meteorological services and other authorised users.
EMADDC
Modern aircraft carry sensors to measure the Mach number (using a pitot static probe) and air temperature. An enhanced surveillance (EHS) air traffic control radar interrogates all aircraft in sight in a selective mode (Mode-S), on which the aircraft replies with a message containing, for example, magnetic heading, airspeed and Mach number. These messages can be collected by Air Traffic Control or by a network of local receivers. The EMADDC use these messages to derive tens of millions of wind and air temperature observations in Europe.
AIREPS, ADS-C, TAMDAR and AFIRS
Additional aircraft based observations are received from AIREPS and ADS-C messages. Third-party data known as TAMDAR and AFIRS AMDAR complement the other networks.
The first meteorological data from aircraft were collected in the early 1900s. Following development of the concept for transmitting aircraft temperature and wind information to the ground in real-time by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology in the 1980’s, European National Met Services (NMHS) started developing their own Aircraft Meteorological Data Relay (AMDAR) Programmes with their national airlines. Each NMHS was then responsible for providing this data to the GTS.
Initial airlines and start dates:
KLM (1993)
Air France (1995)
British Airways (1998)
SAS (1998)
Lufthansa (1999)
Met Office (UK) developed an automated data processing system to handle British Airways data and so the opportunity arose to provide a single processing system for all European AMDAR data.
There are now 15 airlines participating in the E-ABO AMDAR programme and more than 1000 planes providing meteorological data.
Wind and temperature observations derived from ADS-B/MODE-S EHS messages has enhanced the coverage of aircraft based observations over Europe in recent years and is now centralised through the creation of the European Meteorological Derived Data Centre (EMADDC).
OPERA Data production
During the previous OPERA phase (2019-2023), the data centre (ODYSSEY) was gradually replaced with three new production lines (CUMULUS/STRATUS CIRRUS, and NIMBUS).
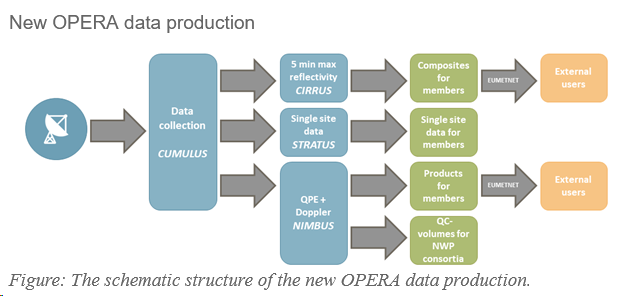
New production lines
• CUMULUS/STRATUS, a real-time data hub providing the incoming data back to members in approximately real-time for their own processing (e.g. regional composites or NWP assimilation) and to the other two production lines (CIRRUS and NIMBUS). The production line has been operational since Q2/2021.
• CIRRUS producing 5-minute instantaneous maximum reflectivity composite (dBZ) for current weather, severe weather alerts and aviation needs. It is replacing the ODYSSEY maximum reflectivity composite with improved spatial (now with 1 km gridding) and temporal resolution (from 15 – minutes to 5- minutes). The production has been operational since Q1/2024. Documentation regarding the CIRRUS maximum reflectivity product and its differences compared to the ODYSSEY maximum reflectivity product can be found here.
OPERA_Max Reflectivity_Product Sheet_Ed-2.0.pdf
OPERA5_Report_Cirrus-vs-Odyssey_Ed-2.0.pdf
• NIMBUS produces centrally the quality-controlled products; instantaneous rain rate (mm/h) and 1 – hour accumulation (mm) composites, and wind profiles (TBD Q4/2024), and additionally the quality-controlled volume data for NWP assimilation. It replaces the ODYSSEY production for the above-mentioned products. The NIMBUS production has been operational since Q2/2024. Documentation regarding the NIMBUS composites and their differences compared to the corresponding ODYSSEY can be found here:
NIMBUS_datasheet_composites_1.0_13062024.pdf
NIMBUS_composite_vs_ODYSSEY_1.0_19062024.pdf
OPERA support can be reached through email to support.opera[at]eumetnet.eu. Responses from the service desk are provided on a best-effort basis.
Access to data
The members of OPERA and EUMETNET may use the composites for their official duties without a separate license. The Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) modelers obtain the quality-controlled volume data directly from the NIMBUS production line.
The OPERA products are also available under license to 3rd parties:
For national weather services not participating in OPERA which want to use the products to support their public weather service, contact info[at]eumetnet.eu
For a research and education licence, contact info[at]eumetnet.eu.
For a license to exploit the products commercially, contact one of the EUMETNET members contact points (https://www.ecomet.eu/contact/members) or send an email to eumetdaps_secretariat[at]eumetnet.eu.
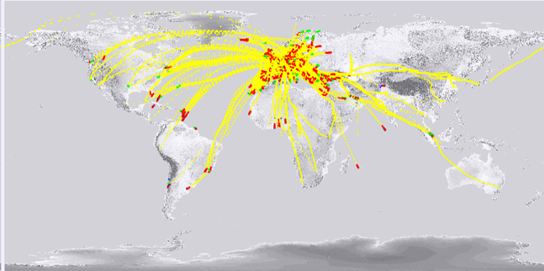
EUMETNET AMDAR coverage
The coverage for the EUMETNET AMDAR network for a typical day is shown on the map below. Yellow plots indicate observations taken enroute with red and green plots representing aircraft ascent and descent profiles.
OBSERVATIONS – OPERA OPERA is the Radar Programme of EUMETNET The objectives of OPERA : The key achievements of OPERA: OPERA has been coordinating radar data exchange in Europe for 20 years, and its data centres have been operational for almost a decade. In the previous programme phase (2019-2023) the data centre (ODYSSEY) operated since 2011, was gradually replaced with three new production lines. The three production lines, CUMULUS/STRATUS, NIMBUS, and CIRRUS, are responsible for gathering the data, and producing European-wide radar products for EUMETNET members as well as third-party users.
During the previous OPERA phase (2019-2023), the data centre (ODYSSEY) was gradually replaced with three new production lines (CUMULUS/STRATUS CIRRUS, and NIMBUS).
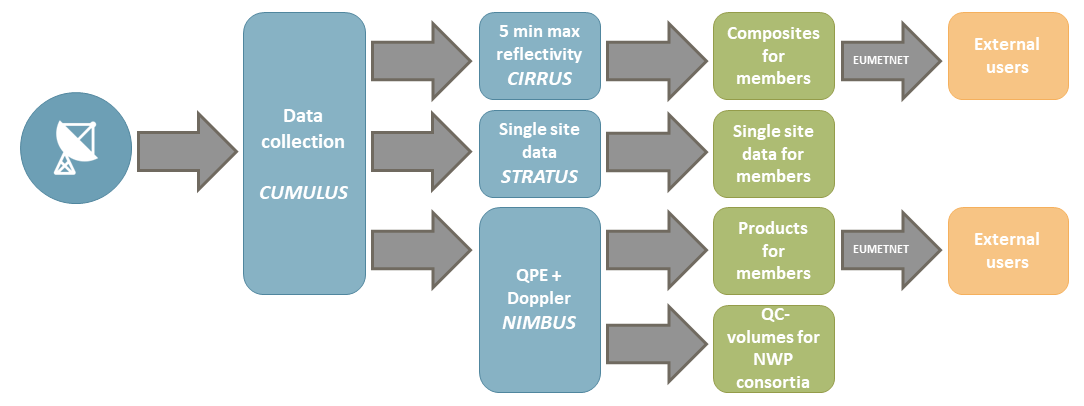
Figure: The schematic structure of the new OPERA data production.
The three new production lines are:
• CUMULUS/STRATUS, a real-time data hub providing the incoming data back to members in approximately real-time for their own processing (e.g. regional composites or NWP assimilation) and to the other two production lines (CIRRUS and NIMBUS). The production line has been operational since Q2/2021.
• CIRRUS producing 5-minute instantaneous maximum reflectivity composite (dBZ) for current weather, severe weather alerts and aviation needs. It is replacing the ODYSSEY maximum reflectivity composite with improved spatial (now with 1 km gridding) and temporal resolution (from 15 – minutes to 5- minutes). The production has been operational in Q1/2024. Documentation regarding the CIRRUS maximum reflectivity product and its differences compared to the ODYSSEY maximum reflectivity product can be found here.
– OPERA_Max Reflectivity_Product Sheet_Ed-2.0.pdf
– OPERA5_Report_Cirrus-vs-Odyssey_Ed-2.0.pdf
• NIMBUS producing centrally the quality-controlled products; instantaneous rain rate (mm/h) and 1 – hour accumulation (mm) composites, and wind profiles (TBD Q4/2024), and additionally the quality-controlled volume data for NWP assimilation. It is replacing the ODYSSEY production for the above-mentioned products. The NIMBUS production has been operational in Q2/2024. Documentation regarding the NIMBUS composites and their differences compared to the corresponding ODYSSEY can be found here:
– NIMBUS_datasheet_composites_1.0_13062024.pdf
– NIMBUS_composite_vs_ODYSSEY_1.0_19062024.pdf
OPERA support can be reached through email to support.opera@emetnet.com. Responses from the service desk are provided on a best-effort basis.
Access to data
The members of OPERA and EUMETNET may use the composites for their official duties without a separate license. The Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) modelers obtain the quality-controlled volume data directly from NIMBUS production line.
The OPERA products are also available under license to 3rd parties:
· For national weather services not participating in OPERA which want to use the products to support their public weather service, contact info@emetnet.com
· For a research and education licence, contact info@emetnet.com.
· For a license to exploit the products commercially, contact one of the EUMETNET members contact points(https://www.ecomet.eu/contact/members) or send a mail eumetdaps_secretariat@emetnet.com.
WG AVIMET: The Working Group for Aviation Objectives Aviation, consisting of a wide spectrum of aeronautical stakeholders, is a high priority customer group for most EUMETNET Members. Via co-operation, EUMETNET Members strive to improve the value and efficiency of aeronautical meteorological services to ensure performance benefits for the aviation industry as well as to reduce the negative impact of adverse weather conditions on the daily operations. AVIMET is a Working Group of EUMETNET that was created to address issues of common interest within the aeronautical meteorological (MET) domain, especially in relation to the ongoing development of the political, technical and regulatory landscape under a Single European Sky (SES). In addition to this, the WG AVIMET aims to facilitate the exchange of information between members on aviation meteorological issues whilst developing common position statements of EUMETNET on aviation-related issues. Focus Areas AVIMET has identified three main focus areas: Membership & Organisation Membership is open to all EUMETNET Members who may nominate one representative to the Working Group. In general, the representative should belong to an authorized and certified MET Service Provider which may be either the EUMETNET Member itself or another agency in that country. On 1st of January 2017 AVIMET has 33 members. The Working Group tasks are coordinated by an elected WG Chairperson whose main roles are to: The AVIMET Chair is assisted by 2 elected Vice-Chairs.
